Work routines in most organizations include several administrative actions that do not require judgment but still occupy time. These repeated tasks interfere with productivity because employees must pause their focus to complete them. The arrival of Copilot Agents in Dynamics 365 offers a practical way to address this challenge. Built to operate within Business Central, these agents interpret structured instructions and carry out defined actions, so people can focus on responsibilities that warrant deliberate thought.
Why standard automation is not always sufficient
Traditional automation depends entirely on fixed rules. When any variation occurs, the system stops and requires user involvement. This approach is helpful for highly repetitive processes, yet it struggles when inputs change slightly or when data relationships must be recognized before action is taken. Copilot Agents address this limitation by applying predefined logic when interpreting context, enabling them to handle tasks beyond rigid templates.
Introducing the agents
Within Dynamics 365 Business Central, several agents built using Copilot Studio demonstrate how structured guidance can drive transactional work. These include:
- Master Data Agents, responsible for creating, updating, and retiring vendor, customer, and item records.
- Purchase Order Agent, which manages procurement-related entries.
- Sales Order Agent, which supports order processing activities.
Each agent focuses on a defined operational area and acts in accordance with existing system rules.
Master data management
Master data updates often pass through multiple people, which slows the transition. The Master Data Agent manages these actions directly. When given a clear prompt, it creates the record, assigns a reference, amends it when required, and removes it when it no longer applies. Its accuracy depends on the clarity of the instruction and on the existing master data structure. Errors usually result from system constraints rather than from inconsistencies in decision-making.

Purchase order handling
Procurement processes are frequently delayed between the decision and entry. The Purchase Order Agent creates the purchase order based on structured input, identifies items, records details, and advances the transaction for posting. User involvement is available when approval or review is necessary, but the majority of data entry occurs without detailed knowledge of procurement screens or configurations.
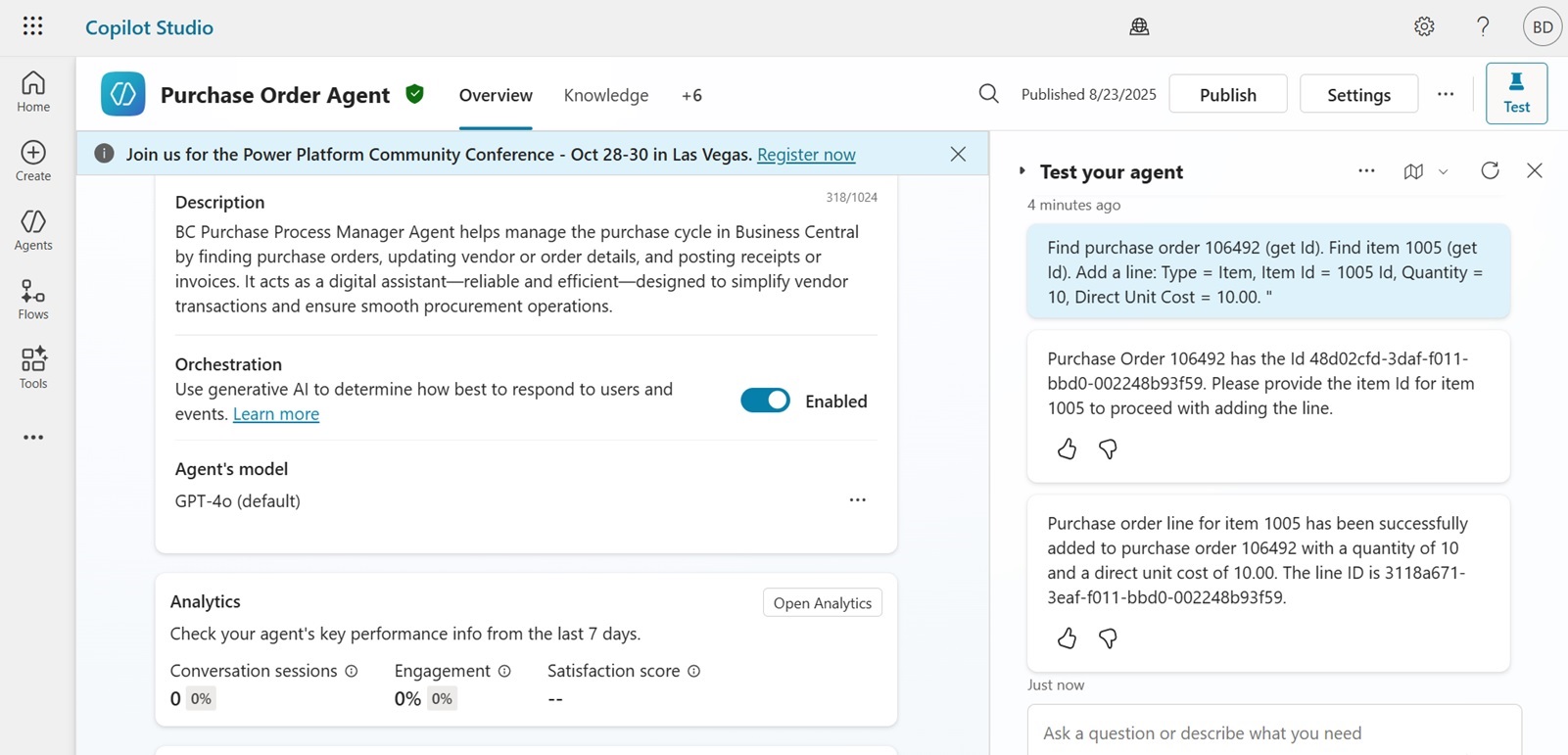
Sales order processing
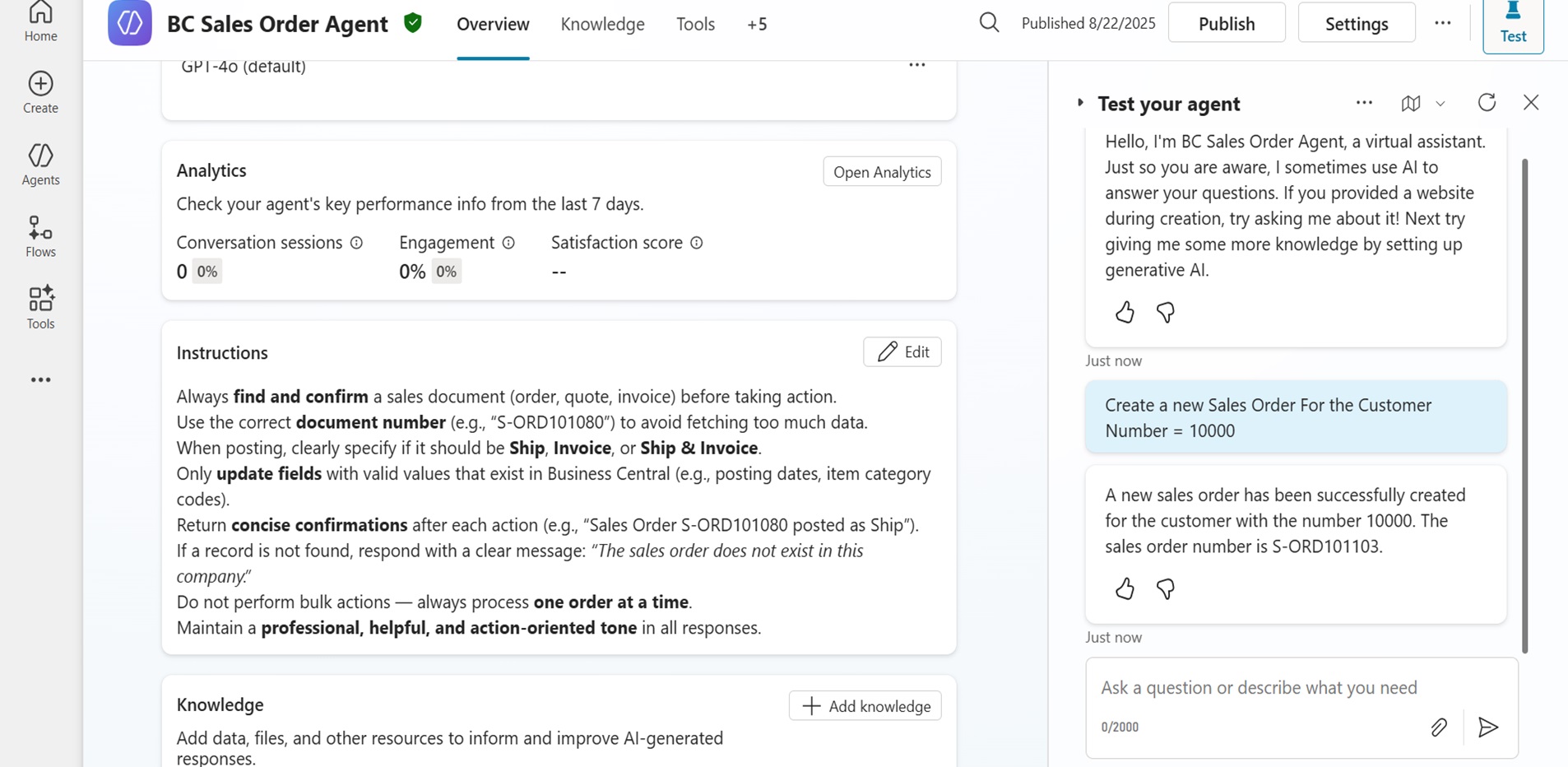
Sales activity often depends on how swiftly basic entries are completed. The Sales Order Agent locates the correct customer, inserts line items, verifies quantities and prices, and progresses the order following system rules. It applies structured prompts to move the record forward without requiring users to navigate multiple screens.
Coordinated agent interaction in a real-world scenario
A practical example is when a new supplier is introduced and an urgent requirement must be fulfilled. Under typical conditions, several employees would intervene across master data administration, procurement, and sales or order flow. Copilot Agents allow these actions to progress as a connected process when clear prompts are provided in sequence.
Sample prompts and actions:
- Vendor onboarding (Master Data Agent)
“Create a new vendor named Global Tech Supplies. Assign vendor number automatically. Contact email: procurement@globaltechsupplies.com. Payment terms: 30 days.”
The agent generates the master record and confirms the allocated reference.
- Item assignment (Master Data Agent)
“Update vendor Global Tech Supplies. Add item code ITM-4520 as an approved supply item. Minimum order quantity: 50 units.”
The agent updates the vendor record and associates the item using relevant parameters.
- Purchase order initiation (Purchase Order Agent)
“Raise a purchase order for vendor Global Tech Supplies. Order 100 units of item ITM-4520. Requested receipt date: 15 June. Unit price: as per last approved quote.”
The record is created, item lines are populated, and the order is advanced for internal review or approval.
- Updating customer request (Sales Order Agent)
“Retrieve sales order SO-1789. Add 100 units of item ITM-4520 with expected shipment date 20 June. Reference purchase order raised today.”
The agent updates the relevant sales order to reflect availability once procurement is completed.
This sequence requires structured input but does not rely on navigating forms or screens. The agents apply existing data relationships, maintain accuracy, and move each task forward without pausing for interface interaction. Users retain control when judgment or approval is required, while the transactional steps progress in a consistent manner.
The role they do not assume
These agents do not have judgment, negotiation, or decision-making authority. They do not alter company policy or bypass approvals. Their role is to manage repetitive entries and maintain consistency across filings and records. Human involvement continues in all areas that depend on evaluation or discretion.
Additional examples
The agents referenced above are representative rather than comprehensive. Additional possibilities include:
- An Invoice Validation Agent that cross-checks entries before posting.
- A Credit Limit Review Agent for updating financial controls in customer accounts.
- A Return Order Agent handling item returns under defined conditions.
- A Stock Adjustment Agent that raises and processes inventory corrections.
- A Forecast Update Agent for revising planning data in Finance and Operations.
All follow the same principle of structured actions within established Dynamics 365 systems.
Closing note
The purpose of these agents is not to replace employees, nor to reduce the importance of human contribution. Their presence allows people to direct their knowledge toward tasks that require consideration instead of repetition. By handling recurring entries with consistency, they support a work environment where time is spent on matters that benefit from attention and experience.
LevelShift can help you integrate Copilot Agents into your workflow. If you wish to explore how these agents can function within your Dynamics 365 Business Central system, our team can demonstrate solutions tailored to your operational practices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
- How do Copilot Agents access and interact with data in Business Central?
They operate within the existing data structure of the Business Central environment. User permissions govern access rights, so the agent can only perform actions authorized by the assigned profile.
- Do these agents affect existing Business Central configurations or extensions?
No. They operate alongside existing configurations and do not modify system design or extension logic. Any action they perform follows the same validation rules as standard transactions.
- How are prompts created for users who are unfamiliar with technical syntax?
Prompts follow clear, descriptive language instead of command syntax. Once guidance is provided, users typically adapt with ease, as the prompts mirror natural workplace instructions.
- What happens if a prompt lacks clarity or contradicts existing data rules?
The agent will not perform the action. It provides a response that highlights the issue, ensuring no unintended data entry or actions occur.
- How are agent actions managed when multiple users submit prompts simultaneously?
Each request is processed independently under the relevant user profile. System controls prevent conflict with ongoing transactions, and standard Business Central governance applies.







